Advanced Imaging Mobile Ultrasound Services
Comprehensive
Ultrasound Imaging
at its best
Medical Ultrasound (also known as diagnostic Sonography or Ultrasonography ) is safe and painless medical imaging. All types of Ultrasound diagnostics do not use ionizing radiation, have no harmful effects, provide images of soft tissues that don’t show up on X-Ray images. And patients likely do not feel any discomfort when the ultrasound probe is placed on their skin.
Color Doppler or Doppler Color Flow (3D Ultrasound) is the presentation of the velocity by color scale. Color Doppler images are generally combined with grayscale (B-mode) images to display Duplex Ultrasonography images, allowing for simultaneous visualization of the anatomy of the area. It allows looking at and examine blood flow speed and direction through arteries and veins in the body, as well as get a comprehensive 3D and 4D representation of the targeted area.
Sonography is a useful way of evaluating the body’s circulatory system. Vascular ultrasound is performed to:
- Help monitor the blood flow to organs and tissues throughout the body
- Locate and identify blockages (stenosis) and abnormalities like plaque or emboli and help plan for their effective treatment
- Detect blood clots (deep venous thrombosis (DVT)) in the major veins of the legs or arms
- Determine whether a patient is a good candidate for a procedure such as angioplasty
- Evaluate the success of procedures that graft or bypass blood vessels
- Determine if there is an enlarged artery (aneurysm)
Doppler’s ultrasound images help to see and evaluate:
- blockages to blood flow (such as clots)
- narrowing of vessels
- tumors and congenital vascular malformations
- reduced or absent blood flow to various organs, such as the testes or ovary
- increased blood flow, as a sign of infection
Click “Learn more” under specific categories to get a comprehensive description and diagnostic assessment guide on each topic.
Arterial Doppler Ultrasonography (Upper and Lower)
Learn more
Arterial Doppler Ultrasound is a type of sonography that used to show and estimate blood flow through blood vessels. Arterial Doppler Ultrasound can help diagnose peripheral vascular diseases: blood clots, poorly functioning valves, blocked arteries, and circulation problems.
Such as (but not limited):
- narrowing or widening of an artery
- superficial thrombophlebitis
- arteriosclerosis
- thromboangiitis obliterans
- vascular tumors in arms or legs
- cystic adventitial
- vasculitis
Indications for Arterial (Color) Doppler Ultrasonography include but are not limited to:
- Having Peripheral arterial disease (PAD) symptoms***
- Claudication pains: painful muscle cramping in the hips, thighs or calves when walking, climbing stairs or exercising, buttocks pain, aching or burning feeling
- Numbness or weakness in arms and legs
- Soreness, tenderness, redness, swelling or warmth; Cold feeling in your lower part of leg or foot
- Pain that does not go away when you stop exercising, swelling
- Change in color and/or shiny skin; Poor nail growth on the toes or hair growth on the legs
- Nonpalpable distal pulses; auscultation of bruits over the iliac, femoral, or popliteal arteries; abnormal capillary refill time
- Erectile dysfunction, especially in men with diabetes
- Inflammatory conditions – swelling in your legs, feet, and/or abdomen
- Abnormalities established by the ankle-brachial index (ABI)
- Musculoskeletal disorders
- History of a blood vessels injury and surgery; Patients being treated for a blood flow disorder.
- Assess a vascular dialysis device (such as an A-V fistula in the arm)
In conjunction with factors of: older age, heart problems, smoking, diabetes mellitus, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, renal insufficiency (glomerular filtration rate less than 60 mL per minute per 1.73 m2), and non-Hispanic black race, a family history of premature CAD.
***Only 10% of patients with PAD have classic claudication; others have atypical leg pain (50%) or are asymptomatic (40%)
Transcranial Doppler Ultrasonography
Learn more
Transcranial Doppler (TCD) and Transcranial Color Doppler (TCCD) measure the velocity of blood flow through the brain’s blood vessels ( arteries known as the Circle of Willis) transcranial (through the cranium). The TCD with combined ColorFlow and Power Doppler allows direct imaging of the intracranial arteries, their anatomic course, diameter, and relationships with the adjacent structures. Effective for detecting sickle cell disease, ischemic cerebrovascular disease, subarachnoid hemorrhage, arteriovenous malformations, syncope, acute ischemic stroke and cerebral circulatory arrest.
The tests are possibly useful for perioperative monitoring and meningeal infection. TCD used as tests to help diagnose emboli, stenosis, vasospasm from a subarachnoid hemorrhage (bleeding from a ruptured aneurysm), and other problems.TCD has important clinical application in the management of patients with sickle-cell disease, brain stem death, and raised intracranial pressure (ICP). Moreover, TCD allows for intraoperative monitoring, evaluation of vasomotor function, and assessment of cerebral microembolism due to right to left cardiac shunts; monitoring of cerebral circulation and embolization during cardiopulmonary bypass, carotid endarterectomies, and carotid artery stenting.
Indications for TCD Sonography include but are not limited to:
- Ischemic cerebrovascular disease
- Numbness or weakness of the face, arm or leg, especially on one side of the body
- Confusion, trouble speaking or understanding; Trouble seeing in one or both eyes
- Trouble walking, dizziness, loss of balance or coordination
- Severe headache with no known cause subarachnoid hemorrhage, double vision, sensitivity to light, or vision loss with or without nausea or vomiting
- Also common: severe headache, abnormal heart rhythm, altered level of consciousness, coma, fainting, seizures, stiff neck, or weakness of one side of the body
- Ischemic stroke
- Vision problems, such as blindness in one eye or double vision weakness or paralysis in your limbs, which may be on one or both sides, depending on the affected artery dizziness and vertigo, confusion, loss of coordination, drooping of face on one side
- Symptoms of embolism
Aorta Doppler Ultrasonography
Learn more
Aorta Doppler Ultrasonography is the first-line imaging study for the diagnosis and the postoperative evaluation and follow-up of patients with diseases of the abdominal great vessels. Color Doppler Sonography provides comprehensive and functional data, which were often unattainable with other methods. Aorta Doppler Ultrasonography is the major diagnostic procedure for the aorta – the largest artery in the body and accordingly, the number 1 diagnostic for Abdominal Aortic aneurysm (AAA).The majority of AAAs are the result of atherosclerosis, which is characterized by the formation of atheromas atheromata, which are raised, fibroadipose plaques that develop within the intimal layer of the artery or within the innermost layers of the tunica media. Apart from arterial thrombosis, embolism, and vasculitis, acute ischemia can also be caused by the simultaneous development of portal hypertension or thrombosis of the superior mesenteric vein.
Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms typically develop slowly over a period of many years and hardly ever cause any noticeable symptoms. Some aneurysms never rupture. Many start small and stay small; others expand over time, some quickly. Occasionally, especially in thin patients, a pulsating sensation in the abdomen may be felt. Acute Mesenteric Ischemia is associated with high mortality rate. The larger an aneurysm grows, the greater the chance it will burst, or rupture, though diagnostics play crucial role in patient well-being.
Indications for Aorta Doppler Ultrasonography include but are not limited to:
- Unexplained lower back pain, flank pain, chest, abdominal area. In some cases in groin, buttocks, or legs. The pain may be deep, aching, gnawing, or throbbing, and it may last for hours or days. Generally it is not affected by movement. Certain positions may be more comfortable than others.
- Palpable or pulsatile abdominal mass or abdominal bruit.
- A “cold foot” or a black or blue painful toe due arterial emboli
- Fever or weight loss caused to inflammatory aortic aneurysm.The symptoms that are similar to the symptoms of coronary artery disease, gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), and peptic ulcer disease.
- Follow-up of a previously demonstrated AAA.
Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm risk factors include: Tobacco use, age 65 and older, being male, white race, family history, having an aneurysm in another large blood vessel.
*Aortic aneurysm burst or rupture, without immediate treatment, can quickly lead to death.
Carotid Doppler Ultrasonography
Learn more
Carotid Doppler Ultrasonography is a powerful modality for evaluating the carotid arteries, (ICA and ECA) – shows the structure and blood movement. Carotid Doppler Ultrasonography is useful not only for detecting carotid artery stenosis but also for detecting atherosclerotic plaque including visualizing the intima media thickness as a biomarker for atherosclerosis.
Carotid Artery Disease (CAD) develops slowly and in many cases, even with a severe blockage, patients experience no symptoms. CAD is a major cause of stroke in the United States. The first sign of the condition may be a stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA).
There are 2 main groups that should be directed for Carotid Doppler Ultrasonography: symptomatic group (which is consist of patients with neurologic incidents such as, patients with the transient ischemic attack, amaurosis fugax, and a minor stroke) and asymptomatic group (which contains patients with cervical bruit, endarterectomy, and neck mass)
Carotid Artery Doppler Sonography should be fully recommended for examination before a major cardiovascular operation, especially coronary artery surgery.
Indications for CCA Doppler Ultrasonography include but are not limited to:
- Bruit Mini-strokes and all transient ischemic attack symptoms (TIA), history of TIA.
- Strokes
- Temporary loss of vision in one eye
- Carotid artery narrowing, known as stenosis
Additional factors:
- Smoking
- High levels of certain fats and cholesterol in the blood
- High blood pressure
- High levels of sugar in the blood due to insulin resistance or diabetes
- A family history of stroke or heart disease
- Tinnitus,
- Increased Heart Rate, Headaches, Blurred Vision, Light-headedness, Poor Balance, Weakness, Loss of Coordination, Lack of exercise, Sleep apnea

Venous Doppler Ultrasound
Learn more
Venous Doppler Ultrasonography is the first choice and often the gold standard imaging technique for the diagnosis of Acute and Chronic Venous diseases. Venous diseases are highly prevalent, mostly caused by valve incompetence and/or obstruction of the vein lumen but signs and symptoms are diverse and unspecific.
Deep venous thrombosis (DVT) is a common disease with potentially serious consequences such as pulmonary embolism (PE). Three factors, namely, blood flow, hypercoagulability, and endothelial injury play and important role in the process of thrombus formation, and they are referred to as Virchow’s Triad
Many of patients referred for Venous Doppler Ultrasonography present with primary superficial varicose veins. Less commonly, lower extremity venous disease is complicated by previous thrombotic events (deep or superficial) resulting in a range of problems in various venous segments including: occlusive or non‐occlusive chronic thrombotic residua, venous wall fibrosis and incompetence of the affected segments. Another distinct group of patients are those representing with recurrent varicose veins following past interventions.
The majority of vessel injuries affect the upper and lower limbs. Vessel injury is a serious problem for physicians, as some vascular lesions may not be initially recognized based on clinical evaluation and vital signs. Thus, Color Doppler Sonography – Venous Duplex Ultrasound (VDUS) is currently considered as the first-line examination for evaluation of vascular injuries, and should be the basis for diagnosis and care.
Venous Doppler Ultrasonography is also used for obtaining venous access, guiding venous procedures, determiningthe immediate outcome of treatment, and short-term and long-term follow-up of patients.
Indications for Venous Doppler Ultrasonography include but are not limited to:
- Suspected upper-extremity deep vein thrombosis / Acute venous thrombosis
- Chronic venous insufficiency
- Chronic venous obstruction-Failure of vein to collapse on direct compression / visualisation of thrombus within lumen / absent or abnormal venous pulsation
- Homan’s signs
- Edema, pain and redness in the legs, tenderness over the calf
- Suspected or healed venous ulcer
- Spider veins (telangiectasias)
- Varicose veins with lower extremity pain or heaviness / Varicose veins with chronic lower extremity swelling or skin changes of chronic venous insufficiency (e.g., hyperpigmentation or lipodermatosclerosis)
- Skin changes of chronic venous insufficiency without visible varicose veins (e.g., hyperpigmentation or lipodermatosclerosis)
- Limb swelling: unilateral (acute) – suspected acute venous thrombosis
Venous Doppler Ultrasonography is use to:
- Evaluation of possible venous thromboembolic disease or venous obstruction in symptomatic or high-risk asymptomatic individuals.
- Assessment of dialysis access
- Assessing competence of valves in deep veins
- Assessment of venous insufficiency, reflux, and varicosities
- Preoperative mapping of saphenous vein / Evaluation of veins prior to venous access,
- After orthopedic surgery
Additional factors: surgery or injury, long-term bed rest or immobility, pregnancy, obesity, a history of venous thrombosis
Doppler Echocardiography
Learn more
Doppler Echocardiography produce accurate assessment of the direction of blood flow and the velocity of blood and cardiac tissue at any arbitrary point. Derived measurements allow assessment of:
- cardiac valve areas and function
- any abnormal communications between the left and right side of the heart
- any leaking of blood through the valves (valvular regurgitation)
- calculation of the cardiac output and calculation of E/A ratio.
An advantage of Doppler Echocardiography is that it can be used to measure blood flow within the heart without invasive procedures. Real-time three-dimensional Echocardiography used to guimde the location of bioptomes during right ventricular endomyocardial biopsies, placement of catheter-delivered valvular devices, and in many other intraoperative assessments.. Echocardiography has become routinely used in the diagnosis, management, and follow-up of patients with any suspected or known heart diseases. List of major conditions for Doppler Echocardiography procedure:
- Atherosclerosis
- Cardiomyopathy
- Congenital heart disease
- Heart failure
- Aneurysm
- Heart valve disease
- Pericarditis
- Pericardial effusion or tamponade
- Atrial or septal wall defects
- Intracardiac Shunts and assessment the heart’s overall function and general structure.
Pelvic Doppler Ultrasound
Learn more
Pelvic Doppler Ultrasonography expose small vessels that could not be seen with real-time technique alone, and an important adjunct in many physiologic and pathologic states, has an important role to play in the diagnosis of early ovarian cancer and identification of palpable masses such as ovarian cysts and uterine fibroids.
Pelvic Doppler can help to see and evaluate blockages to blood flow (such as clots), narrowing of vessels, tumors and congenital vascular malformations, reduced or absent blood flow to various organs such as the testes or ovary; increased blood flow, (which may be a sign of infection).
Over the past decades, pelvic congestion syndrome (PCS) was recognized to be a more common cause of chronic pelvic pain. Approximately one third of all women will suffer from chronic pelvic pain at some point during their lifetime. PCS is associated with what is known as ovarian and pelvic vein dilatation. This can result in varicose veins in the pelvis, thighs, buttock regions or vaginal area. Severe dull aching pain of PCS is thought to be a direct result of the presence of ovarian and pelvic varicosities, much like the leg pain resulting from lower extremity varicose veins.
Indications for Pelvic Doppler Ultrasonography include but are not limited to:
- Dull, aching or “dragging” pain in the pelvis or lower back, particularly on standing and worse around the time of your menstrual period
- Irritable bladder that sometimes leads to stress incontinence
- Irritable bowel (recurrent abdominal pain and diarrhea alternating with periods of constipation)
- Deep dyspareunia (discomfort during or after sexual intercourse)
- Vaginal or vulvar varicose veins (bulging veins around the front passage)
- Varicose veins of the top of the inner thighs or the back of the thighs
Additional fasctors:
- Patients with multiple previous pregnancies
- Weight gain and anatomic changes in the pelvic structures during pregnancy
- Obstructing anatomic anomalie
- Retroaortic left renal vein / Nutcracker phenomenon
- Compression from the right common iliac artery on the left common iliac vein against the spine and pelvic brim.
Pain may be worsened by the following:
Sitting, standing, at the end of the day, during or after intercourse (dyspareunia), or just before the onset of menses. Other symptoms of pelvic congestion are nonspecific and variable in intensity. Affected women may have generalized lethargy, depression, abdominal or pelvic tenderness, vaginal discharge, dysmenorrhea, swollen vulva, lumbosacral neuropathy, rectal discomfort, or urinary frequency.
Chronic Pelvic Pain Differential diagnosis:
- Bowel pathology
- Cancer/metastases
- Endometriosis, Fibroids, Fibromyalgia
- Neurologic pathology
- Orthopedic pathology
- Ovarian cyst
- Pelvic congestion syndrome
- Pelvic inflammatory disorder
- PorphyriaUrologic pathology
- Uterine prolapse
In women, a Pelvic Ultrasound is used to view the:
- Look for growths like noncancerous tumors, fibroids, or cysts
- Discover the cause of abnormal bleeding or pain
- Evaluate or treat fertility problems
- Find problems with the structure of your uterus or ovaries
- Look for cancer in ovaries, uterus, or bladder
- Find an intrauterine device (IUD)
- Monitor your baby’s growth during pregnancy
- Check for pelvic inflammatory disease
- Diagnose an ectopic pregnancy (a fertilized egg that grows outside of the uterus)
- Find a tissue sample to remove from your uterus during an endometrial biopsy
In men :
- Check for problems with the bladder, prostate gland, and seminal vesicles
- Find bladder tumors or stones
Abdominal Doppler Ultrasound
Learn more
Abdominal Doppler Ultrasonography (ADU) facilitates an excellent anatomic display of the abdominal vasculature. Aneurysms and pseudo-aneurysms of visceral arteries are readily differentiated from other cystic lesions. ADU helpful for detection of portal vein thrombosis and stenosis, observation and measurement of splanchnic hemodynamic in patients with chronic liver disease and portal hypertension.
Indications for Abdominal Doppler Ultrasonography include but are not limited to:
- abdominal pain or distention (enlargement),
- pains that presume gallbladder or kidney stones
- pains and symptoms associated with abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA)
- identify the cause of abnormal blood tests
- evidences of abnormal liver function
- check for damage after an injury or the cause of a fever
- fluid retention, swelling of an abdominal organ, increased blood flow (as may be a sign of infection)
- monitor tumors
- examination before / for biopsies
Abdominal Doppler Ultrasonography used to diagnose diseases of the:
- liver, bladder and kidneys
- prostate and uterus
- pancreas, spleen, bile ducts, colon, gallbladder
- adrenal glands
- abdominal aorta and other blood vessels of the abdomen
Conditions such as:
- Abdominal aortic aneurysm
- Abscess Appendicitis
- Cholecystitis and Gallstones
- Hydronephrosis
- Kidney stones
- Pancreatitis (inflammation in pancreas)
- Spleen enlargement (splenomegaly)
- Portal hypertension
- Liver tumors
- Obstruction of bile ducts
- Cirrhosis
Renal Doppler Ultrasound
Learn more
Renal Doppler Ultrasonography is curical for early diagnosis of renovascular disease wich in many cases leads to gradual and silent loss of renal function. Renovascular disease is a complex disorder, most commonly caused by fibromuscular dysplasia and atherosclerotic diseases. It can be found in one of three forms: asymptomatic renal artery stenosis (RAS), renovascular hypertension, and ischemic nephropathy.
Renal Artery Stenosis (RAS) is major casue leading to kidney failure over time. When the process occurs slowly, it leads to secondary hypertension, as the kidney wrongly senses the reduced flow as low blood pressure (via the juxtaglomerular apparatus) and releases a large amount of renin that converts angiotensinogen to angiotensin I. Renal artery stenosis usually does not cause any specific symptoms. Sometimes, the first sign of renal artery stenosis is high blood pressure that is extremely hard to control. Atherosclerotic RAS is a progressive disease, particularly in patients with diabetes or other manifestations of atherosclerosis. Thus, early diagnosis of RAS is an important clinical objective.
The pathologic causes of RAS include:
- atherosclerosis
- fibromuscular dysplasia (FMD)
- arteritis
- dissection and neurofibromatosis
Most the time (~75% of cases), renal artery stenosis is caused by atherosclerosis. The 2nd most common cause (~20%) is fibromuscular dysplasia (FMD).
Renal Artery Stenosis is often found by accident in patients who are undergoing tests for another reason.
Indications for Renal Doppler Ultrasonography include but are not limited to:
- High blood pressure that is extremely hard to control, previously well-controlled high blood pressure, elevated blood pressure that affects other organs in the body
- Whooshing sound as blood flows through a narrowed vessel (bruit), which can be heard through a stethoscope
- Elevated protein levels in the urine or other signs of abnormal kidney function
- Decrease in kidney function during treatment for high blood pressure
- Fluid overload and swelling in your body’s tissues
Additional factors:
- Older age
- Being female
- Having hypertension
- Having other vascular disease (such as coronary artery disease and peripheral artery disease)
- Having chronic kidney disease
- Having diabetes Using tobacco
- Having an abnormal cholesterol level
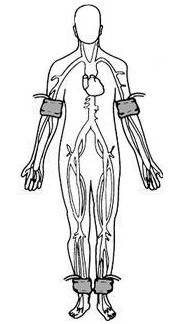
Ankle-brachial pressure index (ABI)
Learn more
Ankle-brachial Pressure Index (ABI) is a key tool in the detection of Peripheral Arterial occlusive Disease (PAD) ( ABPI is 90% with a corresponding 98% specificity for detecting hemodynamically significant (Serious) stenosis >50% in major leg arteries, defined by angiogram).
These so-called peripheral arteries are anything but peripheral. They’re central to good health for the kidneys, intestines, and legs. They are also prone to the same damaging processes that stiffen and clog coronary arteries. Peripheral artery disease causes suffering, disability, and sometimes death among the millions of Americans who have it.
The Ankle-brachial Pressure Index (ABI) also offers information about general cardiovascular health. An analysis of studies including nearly 50,000 men and women show that a low index (under 0.90) doubled the chances of having a heart attack or stroke or dying of heart disease over a 10-year period.
The ABI is performed by measuring the systolic blood pressure from both brachial arteries and from both the dorsalis pedis and posterior tibial arteries after the patient has been at rest in the supine position for 10 minutes. Compared to other diagnostic methods, ABI is superior because it is s a simple, noninvasive test, which could be routinely determined in almost all patients. An important aim of ABI measurement is detection of PAD in asymptomatic patients.
Only 10% of patients with PAD have classic claudication; others have atypical leg pain (50%) or are asymptomatic (40%).
Indications for Ankle-brachial Pressure Index (ABI):
- Assessment of vascular status
- Testing for PAD / Presumption of PAD
- Ulcer Management
- Post-surgical Healing assessment
- History of blunt trauma and knee dislocation
- Diagnose PAD and prevent its progression and complications
- Identify people who have a high risk for coronary artery disease
- Patients of age over 50 and smoker / patients with diabetes, or over age 70
The clinical implications may be summarized as follows:
- Increase awareness of PAD and its negative consequences
- Improve the identification of patients with symptomatic and especially asymptomatic PAD
- Initiate a screening protocol for patients at high risk for PAD
- Increase the rates of early detection among the asymptomatic population
ABI has a very important role in patients with PAD, not only as a diagnostic tool, but also as a negative predictor. Therefore, ABI can be considered a generalized atherosclerotic predictor, identifying patients at high risk for developing cardio- or cerebrovascular events and should be incorporated into routine clinical practice.
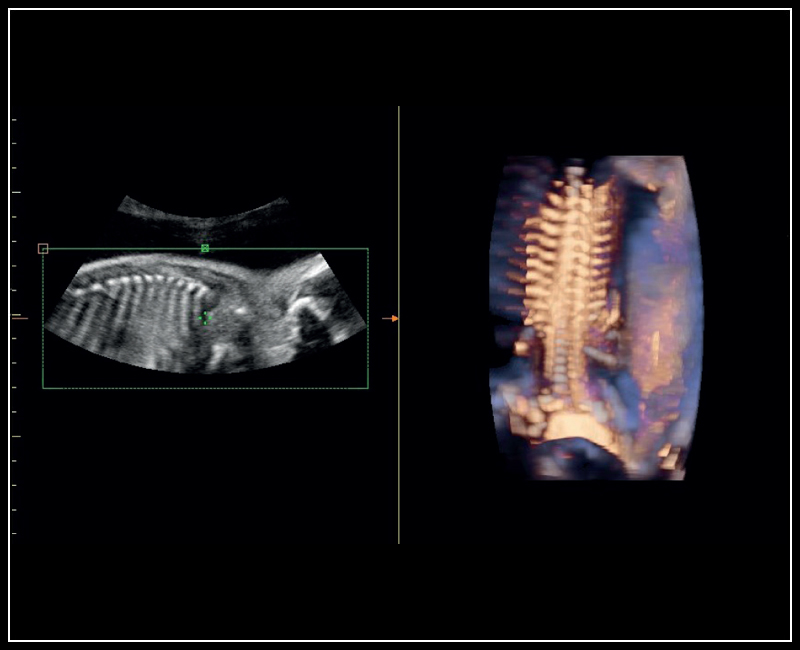
3D / 4D Ultrasound
The latest state-of-the-art equipment
We are using the latest generation of ultrasound diagnostic equipment. It is a smart, superior, multidisciplinary ultrasound unit that allows more efficient, faster, and more complete diagnostics.
And the good news is, thanks to technological progress, equipment no longer require a separate room with tons of devices. It’s all portable!
The majority of ultrasound equipment used in large hospitals and diagnostic facilities made in the mid ’00s. You don’t even need to get in all technical peculiarities to see a distinct advantage of using the latest and up-to-date technology in a crucial aspect of life such as health and well-being. Compare an ordinary piece of tech as a modern smartphone to the cell phones we’ve gotten 20 years ago, what to say about medical equipment.
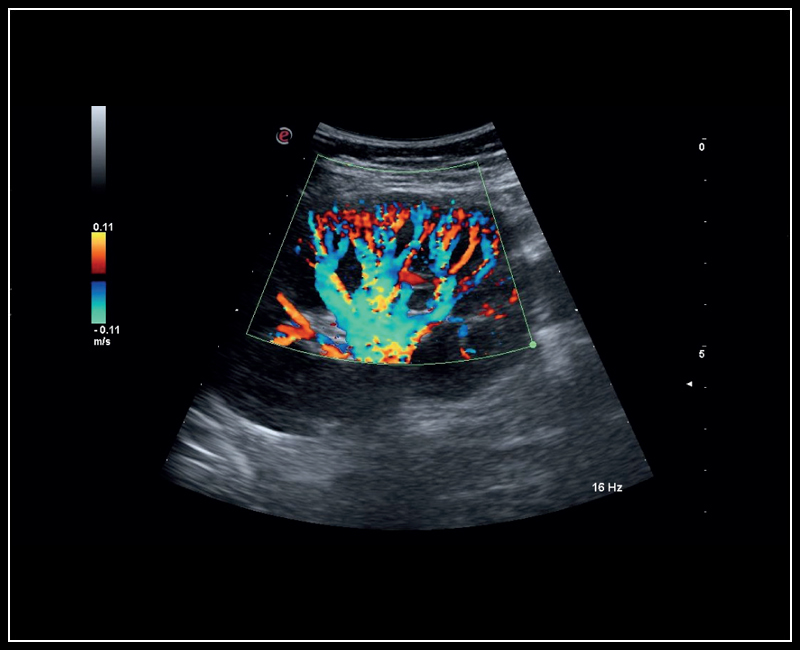
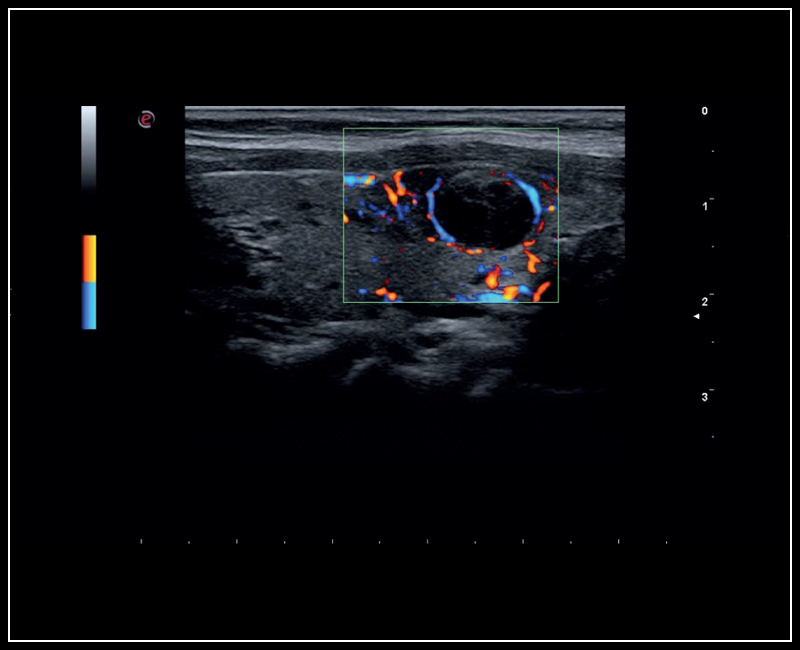
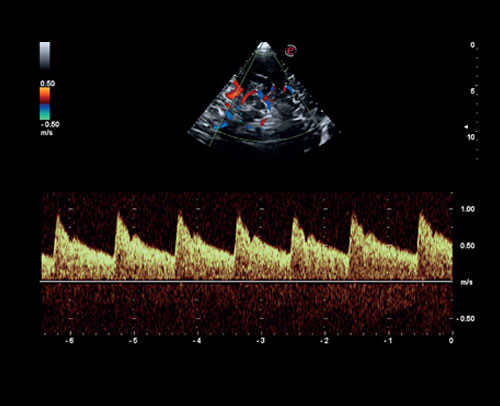
From left to right:
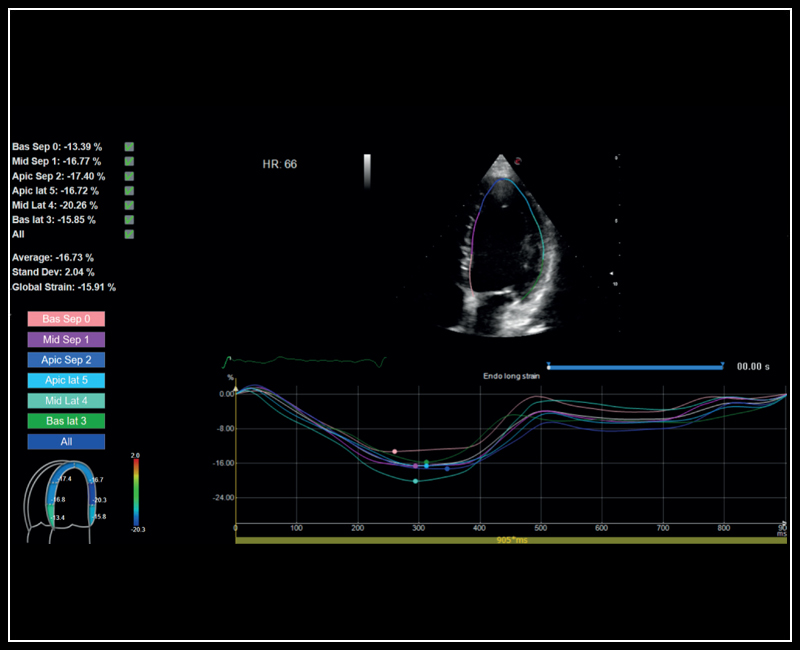
Kidney perfusion with high sensitivity Color Doppler mode | Left Ventricle XStrain 2D analysis
Semi-transparent rendering of fetal | CW Doppler of Tricuspid regurgitation
Thyroid lesion – imaging 2D with Color Doppler | High definition B-mode cardiac imaging
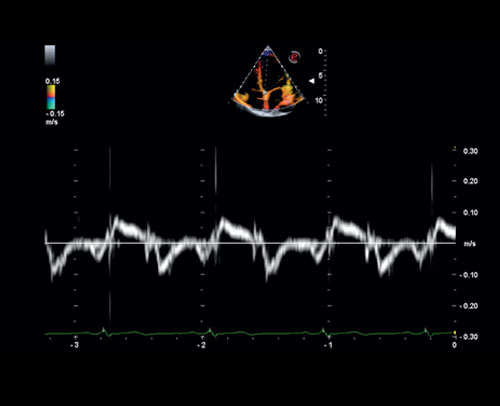
Mid cerebral artery investigation with PW Doppler mode | Mitral valve posterior leaflet analysis with Tissue Velocity Mapping
Secure, private, fast
We run and own private data servers that receive and process all diagnostic and related information. HIPAA Compliant with 128/256-bit Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) encryption — the highest industry standard for online security. Also, readily accessible to all our partners, from here, just a click away.
The fastest report turnover
Modern technological solutions, decades of experience, and outstanding work ethics ensure the fastest report turnover in the industry.